| Title | Size | Downloads |
|---|---|---|
| H3C S5100[S3100] Series Ethernet Switches HSNS Feature Manual(For Soliton)(V1.01).pdf | 173.09 KB |
- Related Documents
-
- H3C Low-End Ethernet Switches Configuration Guide(V1.01)
- H3C Low-End Ethernet Switches Configuration Examples(V1.04)
- H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Installation Manual-(V1.06)
- H3C S3100 Series Ethernet Switches Quick Start(V1.08)
- H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch Operation Manual-Release 1500(V1.02)
- H3C S3100-52P Ethernet Switch Installation Manual(V1.01)
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 HSNS Configuration. 1-1
1.1.2 Typical Networking of HSNS Application. 1-3
1.2.1 HSNS Configuration Task List 1-6
1.2.2 HSNS Common Configuration. 1-7
1.2.3 Configuring HSNS to Work in the DHCP Snooping Mode. 1-8
1.2.4 Configuring HSNS to Work in the 802.1x Mode. 1-9
1.2.5 Configuring HSNS to Work in the MAC Authentication Mode. 1-9
1.2.6 Configuring the ACL Server 1-10
1.2.7 Configuring Fast HSNS with no ACL Server 1-11
1.2.8 Enabling HSNS Globally. 1-12
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining HSNS. 1-13
1.4 HSNS Configuration Example. 1-13
1.4.1 Network Requirements. 1-13
1.4.3 Configuration Procedure. 1-14
Chapter 2 HSNS Configuration Commands. 2-1
2.1 HSNS Configuration Commands. 2-1
2.1.3 display hsns acl-rule. 2-4
2.1.5 hsns default-user-acl 2-7
2.1.8 hsns local-address. 2-10
2.1.11 hsns router-located. 2-12
2.1.12 hsns timer check-mac-address. 2-13
2.1.13 hsns timer keep-alive. 2-14
2.1.14 hsns timer server-timeout 2-14
2.1.16 soliton-dhcp-nap enable. 2-16
Chapter 1 HSNS Configuration
When configuring HSNS, go to these sections for information you are interested in:
1.1 HSNS Overview
H3C - Soliton Network Security (HSNS) is an extension solution co-developed by H3C and Soliton based on Microsoft Network Access Protection (NAP). HSNS is mainly used to work with NAP authentications and perform enhanced authorization (applying ACLs on the port connected to the access user) based on the NAP authentication result.
& Note:
Deployed on Windows Vista/Server 2008 systems, NAP is mainly used to authenticate, authorize and quarantine the access users (i.e., verifying that firewall or antivirus software is enabled) when the client requests access to the network controlled by NAP server and to assign the client the corresponding network segment that can be accessed based on the quarantine result.
At present, you can use HSNS together with DHCP snooping, 802.1x and MAC authentication to control user access privileges.
1.1.1 How HSNS Works
HSNS is jointly implemented by an ACL server and the switch. The local network administrator needs to configure the ACLs for controlling user access (refer to Obtaining an ACL) on the ACL server and configure HSNS on the switch. The switch interacts with the ACL server through Soliton private protocol - Soliton ACL Distribution Protocol (SADP) to perform HSNS authorization for the access client, obtains the ACLs corresponding to the authenticated client and applies them on the port connected to the client, thereby achieving enhanced authorization for the access user.
To perform HSNS authorization, the switch sends the client’s attributes (MAC address, IP address, connected switch port, etc.) to the ACL server. Upon receiving such information, the ACL server looks up authentication status of the client from NAP server, find out configured ACLs for the authenticated user. If such ACLs can be found, they will be passed to the switch to perform enhanced authorization; otherwise, the client will remain unauthorized with default ACLs (refer to hsns default-user-acl).
HSNS works in the following three modes:
l DHCP snooping
l 802.1x
l MAC authentication
In any one of the three modes, HSNS works with DHCP snooping, 802.1x, and MAC authentication respectively to handle the access of legal or restricted users differently.
I. HSNS in the DHCP snooping mode
With DHCP snooping enabled, the switch can analyze the received DHCP packets and records the IP addresses that the DHCP server assigns to the clients, the ports to be used for connecting to the clients, and other information.
Microsoft NAP authenticates the client who is requesting an IP address. If the client fails to pass the authentication, the DHCP server assigns the client an IP address in a restricted network segment and sends back DHCPACK packets carrying static routes to the restricted network.
When HSNS works in the DHCP snooping mode, the switch determines whether a client passes NAP authentication based on whether the DHCPACK packet carries a restricted subnet mask option.
l The client passes NAP authentication if the DHCPACK packet carries restricted subnet mask option.
l The client failed to pass NAP authentication if the DHCPACK packet carries unrestricted subnet mask option.
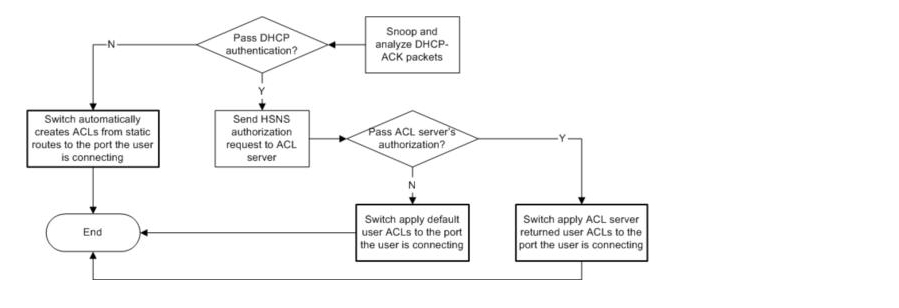
As shown in Figure 1-1, the switch works with the ACL server to obtain the configured ACLs and apply them on the port connected to the client, thereby enhancing user authorization.
Figure 1-1 HSNS working flow on the switch
After analyzing the DHCPACK packets, updating the authentication information, the switch forwards DHCPACK to the client to ensure that the client can obtain the requested IP address normally. When a DHCPACK shows that the user can enter an unrestricted network, switch will perform HSNS enhanced authorization to request user ACLs.
II. HSNS in the 802.1x mode
HSNS can perform HSNS authorization on an 802.1x-authenticated user through the ACL server:
l For an HSNS authorized user, the ACL server sends back the configured ACLs to the switch and the switch applies the ACLs on the port connected to the user.
l For a user who has not passed the HSNS authorization, the switch automatically creates an ACL based on the default user ACL setting, the user will remain 802.1x-authenticated.
& Note:
A user who is 802.1x-authenticated but not HSNS-authorized may be unable to access the network even though the 802.1x client software shows that the user is authorized. In this case, you can use the display hsns client command and check whether the user has passed the HSNS authentication.
III. HSNS in the MAC authentication mode
HSNS can perform HSNS authorization on a MAC-authenticated user through the ACL server:
l For a HSNS-authorized user, the ACL server sends back the specified ACL to the switch and the switch applies the ACL on the port connected to the user.
l For a user who has not passed the HSNS authorization, the switch automatically creates an ACL based on the default user ACL setting, the user will remain MAC-authenticated.
1.1.2 Typical Networking of HSNS Application
I. HSNS networking modes
There are two HSNS networking modes:
l Layer-2 mode: The client is directly connected to the switch, and the switch directly forwards the DHCP request packets sent by the client or performs 802.1x authentication/MAC authentication on the client. Figure 1-2 illustrates this networking mode.
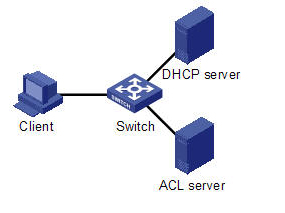
Figure 1-2 HSNS networking in Layer-2 mode
l Layer-3 mode: The client is connected to the switch through the DHCP relay agent. In this mode, the switch cannot perform 802.1x or MAC authentication on the client and HSNS can work with DHCP snooping only. Figure 1-3 illustrates this networking mode.
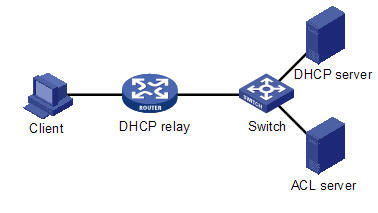
Figure 1-3 HSNS networking in Layer-3 mode
Layer-2 and Layer-3 networking modes differ as follows:
l In the Layer-2 mode, the MAC address of the client and the IP address that DHCP server assigned to the client can be bound in the ACLs to be applied to the user. HSNS periodically checks whether the MAC address of the user still exists in the MAC address table of the switch. If HSNS detects that the user MAC address has aged out, the corresponding ACLs are removed.
l In the Layer-3 mode, only the IP address of the client can be bound in the ACLs applied to the user, and the ACLs aging timer is the IP address lease time specified in the DHCPACK packets.
II. Uplink ports of HSNS
The uplink ports of HSNS are the switch ports connected to the DHCP server, ACL server, external network, patch server, and other non-client devices. For HSNS to work with DHCP snooping, you need to configure the trusted ports of DHCP snooping as the uplink ports of HSNS.
1.1.3 Obtaining an ACL
I. Using the ACL server
& Note:
This section only describes how the switch obtains ACLs from the ACL server. For the configuration of ACL rules on the ACL server, refer to the parts discussing the ACL server software.
For HSNS, the network administrator can configure two ACL servers for switch, one as the primary server and the other the secondary server.
After being configured with ACL servers, the switch maintains the connection to the ACL servers by periodically sending them keep-alive packets. If the switch receives no response from the ACL servers, the switch retransmits the keep-alive packets. If the switch still receives no response from the ACL servers after the specified number of keep-alive packet transmission attempts, the switch considers the server down.
To perform HSNS authentication on a user through an ACL server, the switch sends the authentication request to the primary ACL server first. If the switch receives no response from the server within the server packet timeout time, the switch retransmits the request. If the switch still receives no response after the maximum number of transmission attempts, the switch performs a primary/secondary ACL server switchover and sends the request to the new primary server, namely, the secondary server before the switchover. If neither server gives any responses, the switch takes one of the following actions based on default user ACL configurations (refer to hsns default-user-acl):
l Permit all: Switch will apply a default user ACL indicating the user has full access privilege to the network.
l Deny all: Switch will delete all user ACLs, which means the user has not any access privilege to the network if there are denial ACLs with lower priority than user ACLs configured for the port.
Such default user ACLs will be applied if one of following conditions is matched:
l Connection timeout: HSNS enters emergency mode due to no response from any of the configured ACL servers.
l No resource: HSNS enters emergency mode due to the number of configured switch wide system ACLs are too large than HSNS can handle.
l ACL request timeout: whenever there’s no reply or timeout occurs when HSNS is trying to request ACLs for the authenticated user.
l ACL resource limitation: whenever the reply from ACL server contains too large amount of ACLs that HSNS can handle.
II. Using fast HSNS with no ACL server
& Note:
Fast HSNS with no ACL server can only work with DHCP snooping mode.
To simplify user configuration, switch provide fast HSNS without the need of configuring ACL servers. With fast HSNS configured, the switch automatically creates the user ACLs based on the contents of the DHCPACK packets, instead of sending the request for authenticating the HSNS user through the ACL server.
l If the DHCPACK packets carry restricted subnet mask option, it means the user has not passed the NAP authentication. In this case, the switch automatically creates ACLs to allow the user only the access to the network reachable through static routes carried by the DHCPACK, thus restricting the user's network access.
l If the DHCPACK packets contain subnet mask option showing client’s access has been restricted, this means the user has passed the NAP authentication. In this case, the switch creates ACLs to allow the user’s unrestricted access to the network.
& Note:
The contents of the ACLs automatically generated by the switch vary with networking modes. For details, refer to Typical Networking of HSNS Application.
1.2 HSNS Configuration
1.2.1 HSNS Configuration Task List
Complete the following tasks to configure HSNS:
To do… | Remarks |
Required | |
Required Perform any of the configurations | |
Required Perform either configuration | |
Required |
& Note:
The command line keyword hsns used in HSNS configuration is the acronym of H3C Soliton Network Security.
1.2.2 HSNS Common Configuration
Follow these steps to perform HSNS common configuration:
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
Enter system view | system-view | — |
Enter Ethernet port view | interface interface-type interface-number | — |
Configure the HSNS networking mode of the port as the Layer-3 mode | hsns router-located | Optional Layer-2 mode by default |
Configure the port as an uplink port of HSNS | hsns uplink-port | Required By default, no port is an uplink port of HSNS. You need to configure the switch ports connected to the DHCP server, ACL server, and other non-client appliances as HSNS uplink ports. |
Return to system view | quit | — |
Force the user offline | hsns cut client { all | ip ip-address | mac mac-address | interface interface-type interface-number } | Optional If the user's client becomes abnormal but the user does not go offline, you can use this command to remove the ACL applied on the user to reduce system resource consumption. |
Configure the interval at which HSNS checks the user MAC address entries | hsns timer check-mac-address time | Optional 300 seconds by default |
& Note:
l The HSNS networking mode and the interval at which HSNS checks user MAC address entries take effect only if they are configured before HSNS is enabled globally.
l You cannot configure the networking mode on a port configured as an uplink port of HSNS.
l If you configure the networking mode of a port as the Layer-3 mode when configuring HSNS to work in the DHCP snooping mode, you need to configure the port as a DHCP snooping trusted port to ensure normal HSNS operation. For detailed configuration of a DHCP snooping trusted port, see the part discussing DHCP snooping in this manual.
1.2.3 Configuring HSNS to Work in the DHCP Snooping Mode
I. Configuration prerequisites
Complete HSNS common configuration before configuring HSNS to work in the DHCP snooping mode.
II. Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure HSNS to work in the DHCP snooping mode
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
Enter system view | system-view | — |
Enable DHCP snooping globally | dhcp-snooping | Required Disabled by default |
Configure HSNS to work in the DHCP snooping mode | hsns mode dhcp-snooping | Optional By default, HSNS works in the DHCP snooping mode. |
& Note:
l To configure HSNS to work in the DHCP snooping mode, you are recommended to configure the DHCP snooping trusted ports as HSNS uplink ports.
l For details about DHCP snooping and DHCP snooping trusted ports, refer to the parts discussing DHCP snooping in this manual.
1.2.4 Configuring HSNS to Work in the 802.1x Mode
I. Configuration prerequisites
Complete HSNS common configuration before configuring HSNS to work in the 802.1x mode.
II. Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure HSNS to work in the 802.1x mode:
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
Enter system view | system-view | — |
Disable 802.1x handshake globally | undo dot1x handshake enable | Required By default switch use handshake packets to keep-alive with 802.1x clients. This should be disabled for HSNS. |
Enable 802.1x globally | dot1x | Required Disabled by default |
Configure HSNS to work in the 802.1x mode | hsns mode dot1x | Required By default, HSNS works in the DHCP snooping mode. |
Enter Ethernet port view of the port connected to the client | interface interface-type interface-number | — |
Enable 802.1x on the port | dot1x | Optional Disabled by default |
& Note:
For 802.1x configuration, refer to the parts discussing 802.1x and System-guide in this manual.
1.2.5 Configuring HSNS to Work in the MAC Authentication Mode
I. Configuration prerequisites
Complete HSNS common configuration before configuring HSNS to work in the MAC authentication mode.
II. Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure HSNS to work in the MAC authentication mode
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
Enter system view | system-view | — |
Enable MAC authentication globally | mac-authentication | Required Disabled by default |
Configure HSNS to work in the MAC authentication mode | hsns mode mac-authentication | Required By default, HSNS works in the DHCP snooping mode. |
Enter Ethernet port view of the port connected to the client | interface interface-type interface-number | — |
Enable MAC authentication on the port | mac-authentication | Optional Disabled by default |
& Note:
For MAC authentication configuration, refer to the parts discussing MAC authentication in this manual.
1.2.6 Configuring the ACL Server
& Note:
This section discusses only the parameter configurations for connecting the switch to the ACL server. For the configuration of HSNS authentication and ACL operations on the ACL server, refer to the parts discussing the ACL server software.
Follow these steps to configure the ACL server:
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
Enter system view | system-view | — |
Configure the IP address of the ACL server and the UDP port to be connected | hsns acl-server { primary | secondary } ip ip-address [ port port-number ] | Required Not configured by default |
Configure the local port IP address and UDP port of the switch to be used for communicating with the ACL server | hsns local-address ip ip-address [ port port-number ] | Optional The switch uses the egress interface address destined for the network segment of the ACL server as the local address to be used for communication with the ACL server and uses port 45899 as the UDP service port. |
Configure the packet timeout time of the ACL server | hsns timer server-timeout time | Optional 10 seconds by default |
Configure the interval at which the switch sends keepalive packets to the ACL server | hsns timer keep-alive time | Optional 60 seconds by default |
Configure the maximum number of packet transmission attempts from the switch to the ACL server | hsns retry times | Optional 3 times by default This argument takes effect on keepalive packets and HSNS authentication packets. |
Configure the action to be taken when the HSNS cannot obtain user ACLs from ACL server | hsns default-user-acl { deny-all | permit-all } | Optional permit-all by default |
& Note:
l The IP address of the ACL server must be a valid unicast address but not an all-zero address, broadcast address, multicast address, or loopback address.
l When HSNS works in the DHCP snooping mode, the ACL server timeout time (packet timeout time × number of packet transmission attempts) must not be greater than the DHCP request timeout time of the client (if the primary/secondary ACL servers are configured, the sum of the timeout time of the two servers must not be greater than the DHCP request timeout time of the client); otherwise, the client will be unable to receive any DHCPACK packets and HSNS will fail.
1.2.7 Configuring Fast HSNS with no ACL Server
I. Configuration prerequisites
Do not enable HSNS before configuring fast HSNS with no ACL server.
II. Configuration procedure
Follow these steps to configure fast HSNS with no ACL server
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
Enter system view | system-view | — |
Configure fast HSNS with no ACL Server | soliton-dhcp-nap enable | Required Not configured by default |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l Fast HSNS with no ACL server can work with only DHCP snooping mode.
l This configuration changes the existing HSNS configuration on the switch. It automatically enables HSNS and configures itself to work in DHCP snooping mode, deletes the existing ACL server configuration, and automatically configures the port [Gigabit]Ethernet 1/0/1 (interface name is variant based on switch model) of the switch as a HSNS uplink port if no uplink port is specified. In addition, canceling this function does not automatically restore these configurations.
l Fast HSNS will not automatically configure settings of DHCP snooping, local system administrators are required to configure DHCP snooping mode (i.e. dhcp-snooping trust / dhcp-snooping) before enabling fast HSNS mode.
1.2.8 Enabling HSNS Globally
Follow these steps to enable HSNS globally:
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
Enter system view | system-view | — |
Enabling HSNS globally | hsns enable | Required Disabled by default |
![]() Caution:
Caution:
l Other HSNS-related configurations take effect only if they are made before HSNS is enabled globally. You cannot change this configuration after HSNS is enabled globally.
l Before enabling HSNS globally, verify that the connection between the switch and the ACL server is normal; otherwise, HSNS cannot be enabled.
l Configure HSNS uplink ports before enabling HSNS globally.
1.3 Displaying and Maintaining HSNS
To do… | Use the command… | Remarks |
display hsns | Available in any view | |
display hsns client { all | ip ip-address | mac mac-address | interface interface-type interface-number } | ||
Display applied ACL rules | display hsns acl-rule | Available in system view |
1.4 HSNS Configuration Example
1.4.1 Network Requirements
NAP-DHCP quarantine is implemented on Microsoft Windows XP SP3, Windows Vista and Server 2008 systems in a local area network. At present, HSNS needs to be configured to work in the DHCP snooping mode to meet the following requirements:
l The switch obtains the desired ACL from the ACL server (the primary server 10.220.0.100 or the secondary server 10.220.0.133, both on port 49899) and applies it on the port connected to the client passing NAP authentication, allowing the client access to all the resources in the network.
l The switch allows the client that has not passed NAP authentication only restricted access to the network resources.
l The switch uses the following parameter configuration for the connection to the ACL server:
Table 1-1 Parameter configurations of the switch
Parameter | Configuration |
Local IP address and port that the switch uses for the connection to the ACL server | l IP address: 10.220.0.1 l Port: 45000 |
Timeout time of the packets sent by the ACL server | 15 seconds |
Maximum number of packet transmission attempts to the ACL server | 5 times |
Action to be taken when HSNS cannot apply user ACLs from ACL server | Deny all |
Interval at which HSNS checks user MAC address entries | 60 seconds |
1.4.2 Network Diagram
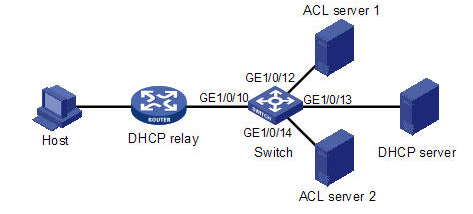
Figure 1-4 Network diagram for typical HSNS configuration
1.4.3 Configuration Procedure
# Create a VLAN interface with an IP address of 10.220.0.1 on the switch.
<H3C> system-view
[H3C] interface Vlan-interface 1
[H3C-Vlan-interface1] ip address 10.220.0.1 255.255.255.0
[H3C-Vlan-interface1] quit
# Configure the HSNS networking mode on the port connected to the DHCP relay agent as Layer-3 mode.
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/10
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/10] hsns router-located
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/10] quit
# Configure the ports connected to the DHCP server and the ACL server as HSNS uplink ports.
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/12
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] hsns uplink-port
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/12] quit
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/14
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/14] hsns uplink-port
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/14] quit
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/13
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/13] hsns uplink-port
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/13] quit
# Configure the interval at which HSNS checks user MAC address entries.
[H3C] hsns timer check-mac-address 60
# Enable DHCP snooping and configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/10 and GigabitEthernet 1/0/13 as a DHCP snooping trusted port.
[H3C] dhcp-snooping
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/10
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/10] dhcp-snooping trust
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/10] quit
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/13
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/13] dhcp-snooping trust
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/13] quit
# Configure HSNS to work in the DHCP snooping mode.
[H3C] hsns mode dhcp-snooping
# Specify the IP addresses and port numbers of the primary and the secondary ACL servers.
<H3C> system-view
[H3C] hsns acl-server primary ip 10.220.0.100 port 49899
[H3C] hsns acl-server secondary ip 10.220.0.133 port 49899
# Specify the IP address and port that the switch uses for connection to the ACL server.
[H3C] hsns local-address ip 10.220.0.1 port 45000
# Configure the packet timeout time and the maximum number of packet transmission attempts of the switch for the connection to the ACL server.
[H3C] hsns timer server-timeout 15
[H3C] hsns retry 5
# Configure the action to be taken when HSNS cannot apply user ACLs from ACL server.
[H3C] hsns default-user-acl deny-all
# Enable HSNS.
[H3C] hsns enable
# Display the existing HSNS configuration.
[H3C] display hsns
HSNS State: Enable
ACL server primary: IP=10.220.0.100 Port=49899 Active
ACL server secondary: IP=10.220.0.133 Port=49899 Up
Local address: IP=10.200.0.1 Port=45000
Timer timeout: 2(s)
Retry: 5
Timer keep-alive interval: 60(s)
Timer check-mac-address: 60(s)
Mode: dhcp-snooping
Default-user-acl: deny-all
Interface Configuration:
Interface number Configuration
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/2 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/3 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/4 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/5 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/6 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/7 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/8 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/9 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/10 Router-located
GigabitEthernet1/0/11 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/12 Uplink
GigabitEthernet1/0/13 Uplink
GigabitEthernet1/0/14 Uplink
GigabitEthernet1/0/15 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/16 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/17 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/18 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/19 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/20 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/21 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/22 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/23 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/24 -
-: Default configuration
The display above shows that all the HSNS-related configurations have taken effect.
Chapter 2 HSNS Configuration Commands
2.1 HSNS Configuration Commands
2.1.1 display hsns
Syntax
display hsns
View
Any view
Parameters
None
Description
Use the display hsns command to display the HSNS configuration information.
Examples
# Display the current HSNS configuration information.
<H3C> display hsns
HSNS State: Enabled
ACL server primary: IP=10.220.0.100 Port=49899 Active
ACL server secondary: IP=10.220.0.133 Port=49899 Up
Local address: IP=10.200.0.1 Port=45000
Timer timeout: 2(s)
Retry: 5
Timer keep-alive interval: 60(s)
Timer check-mac-address: 60(s)
Mode: dhcp-snooping
Default-user-acl: deny-all
Interface Configuration:
Interface number Configuration
GigabitEthernet1/0/1 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/2 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/3 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/4 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/5 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/6 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/7 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/8 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/9 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/10 Router-located
GigabitEthernet1/0/11 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/12 Uplink
GigabitEthernet1/0/13 Uplink
GigabitEthernet1/0/14 Uplink
GigabitEthernet1/0/15 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/16 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/17 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/18 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/19 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/20 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/21 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/22 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/23 -
GigabitEthernet1/0/24 -
-: Default configuration
Table 2-1 Description on the fields of the display hsns command
Field | Description |
HSNS State | Current HSNS state: enabled or disabled. |
ACL server primary | IP address and UDP port of the primary ACL server |
ACL server secondary | IP address and UDP port of the secondary ACL server |
Active | This ACL server is up and being used. |
Up | This ACL server is up but not being used (An ACL server displayed as Down is not usable). |
Local address | Interface IP address and UDP port used to receive the packets from the ACL server |
Timer timeout | Packet timeout time of the ACL server |
Retry | Maximum number of packet transmission attempts for connection to the ACL server |
Timer keep-alive interval | Interval at which the switch sends keepalive packets to the ACL server |
Timer check-mac-address | Interval at which the switch checks user MAC address entries |
Mode | HSNS working mode: dhcp-snooping, dot1x, or mac-authentication. |
Default-user-acl | Action to be taken when HSNS cannot apply user ACLs from ACL server: deny-all or permit-all |
Interface Configuration | Port configuration. Interface number means port number. Configuration means the current port configuration (- means the default configuration, namely, the port is working in Layer-2 mode; Router-located means the port is working in Layer-3 mode; Uplink means the port is configured as an uplink port). |
Router-located | The HSNS networking mode on the port is Layer-3 mode |
Uplink | The port is configured as a HSNS uplink port. |
2.1.2 display hsns client
Syntax
display hsns client { all | interface interface-type interface-number | ip ip-address | mac mac-address }
View
Any view
Parameters
all: Displays the information about all the HSNS clients.
interface interface-type interface-number: Displays the information about the client connected to the specified interface. Use the interface-type interface-number argument to specify the type and number of the port connected to the client
ip ip-address: Displays the information about the client with the specified IP address. Use the ip-address argument to specify a client IP address, in dotted decimal notation.
mac mac-address: Displays the information about the client with the specified MAC address. Use the mac-address argument to specify a client MAC address, in the H-H-H format.
Description
Use the display hsns client command to display HSNS client information.
Examples
# Display the information about all the HSNS clients.
<H3C> display hsns client all
IP MAC Online-time(s) Interface State
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
192.168.6.123 000d-5678-0123 1204 GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Online
192.168.6.22 000d-56a8-012e 2546 GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Unauthorized
192.168.6.132 000d-ab78-0c2e 3612 GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Unauthenticated
192.168.6.131 000d-ab78-0c2f 3622 GigabitEthernet1/0/1 Unauthorized
Total 4 clients matched.
Table 2-2 Description on the fields of the display hsns command
Field | Description |
IP | Client IP address |
MAC | Client MAC address |
Online-time(s) | Length of time the client has been online, in seconds |
Interface | Interface connected to the client |
State | Current state of the client l Unauthenticated means the client has not passed authentication for the configured networking mode. l Unauthorized means the client has not passed ACL server’s authorization. l Online means the client has not passed ACL server’s authorization. |
2.1.3 display hsns acl-rule
Syntax
display hsns acl-rule { system | user-mac mac-address }
View
Any view
Parameters
system: Displays applied switch wide system ACL rules.
user-mac mac-address: Displays applied ACL rules about the client with the specified MAC address. Use the mac-address argument to specify a client MAC address, in the H-H-H format.
Displays all applied ACL rules on the switch when none of above parameters are given.
Description
Use the display hsns acl-rule command to display currently applied ACL rules.
Examples
# Display the applied ACLs.
[H3C] display hsns acl-rule
System ACL:( From-Server )
1 : Pri H, Action permit, Port NON-UPLINK
L4Pro 0x11, DPORT 67-67,
2 : Pri H, Action permit, Port NON-UPLINK
L3Pro 0x0806,
3 : Pri L, Action deny, Port NON-UPLINK
User ACL:
1 : Pri M, Action permit, Port GigabitEthernet1/0/6
L4Pro 0x01,
SrcMAC 001a-a0be-91dd,
SrcIP 192.168.1.110 255.255.255.255,
2 : Pri M, Action permit, Port GigabitEthernet1/0/6
DPORT 80-80,
SrcMAC 001a-a0be-91dd,
SrcIP 192.168.1.110 255.255.255.255,
User ACL:
1 : Pri M, Action permit, Port GigabitEthernet1/0/8
DPORT 80-80,
SrcMAC 0019-db73-d8ce,
SrcIP 192.168.1.104 255.255.255.255,
Table 2-3 Description on the fields of the display hsns command
Field | Description |
System ACL | Switch wide system ACLs, following two types of ACLs will be displayed: l From Server means the ACL is applied from ACL server returned ACLs. l Default ACL means the ACL is applied according to the local default settings. |
User ACL | User ACLs will be applied to the port the authenticated client is connected to, following two types of ACLs will be displayed: l From Server means the ACL is applied from ACL server returned ACLs. l Default ACL means the ACL is applied according to the local default settings. |
Pri | ACLs priority l H means the highest priority; such ACLs are known as Pre-ACLs. l L means the lowest priority; such ACLs are known as Post-ACLs. l M means the medium priority; such ACLs are always user ACLs. |
Action | Action to be taken when the ACL matches a packet l permit means the packet will be forwarded. l deny means the packet will be dropped. |
Port | Switch port this ACL applies for. Following key words may appear with system ACLs: l NON-UPLINK means all switch ports except the uplink ports. l ALL-PORT means all switch ports. |
EthType | Ethernet protocol type |
IPPro | Ipv4 protocol type |
SrcMAC | Source MAC address |
DesMAC | Destination MAC address |
SrcIP | Source Ipv4 address and network mask |
DesIP | Destination Ipv4 address and network mask |
SPORT | Source port |
DPORT | Destination port |
2.1.4 hsns acl-server
Syntax
hsns acl-server { primary | secondary } ip ip-address [ port port-number ]
undo hsns acl-server { primary | secondary }
View
System view
Parameters
primary: Specifies the primary ACL server IP address and port to be used for connections.
secondary: Specifies the secondary ACL server IP address and port to be used for connections.
ip ip-address: Specifies an ACL server IP address, in dotted decimal notation.
port port-number: Specifies the UDP port to be used by the ACL server. The value of port-number is in the range 1 to 65535. By default, the switch is connected to port 45899 of the ACL server.
Description
Use the hsns acl-server command to specify the ACL server IP address and the UDP port to be used.
Use the undo hsns acl-server command to cancel the ACL server configuration.
By default, no ACL server is specified.
& Note:
l The IP address of the ACL server must be a valid unicast address but not an all-zero address, broadcast address, multicast address, or loopback address.
l The IP addresses and port numbers of the primary and secondary ACL servers must not be the same at the same time.
Examples
# Configure the primary ACL server IP address and the UDP port number to be used as 192.168.0.1 and 45000, respectively; configure the secondary ACL server IP address and the UDP port number to be used as 192.168.0.33 and 34480, respectively.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns acl-server primary ip 192.168.0.1 port 45000
[H3C] hsns acl-server secondary ip 192.168.0.33 port 34480
2.1.5 hsns default-user-acl
Syntax
hsns default-user-acl { deny-all | permit-all }
undo hsns default-user-acl
View
System view
Parameters
deny-all: Denies all the user accesses when HSNS cannot apply user ACLs configured in the ACL server. That is, no ACL is applied so that the user cannot access the network.
permit-all: Permits all the user accesses when cannot apply user ACLs configured in the ACL server. That is, the default ACL is applied to allow the users unrestricted access to the network.
Description
Use the hsns default-user-acl command to specify the action that the switch will take on the client when the user ACL from server cannot be applied.
Use the undo hsns default-user-acl command to restore the default.
By default, the switch denies all the accesses from the client after the connection to the ACL server times out.
Related command: hsns timer server-timeout, hsns retry.
Examples
# Configure the switch to permit all the accesses from the client when the user ACL from server cannot be applied.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns default-user-acl permit-all
2.1.6 hsns cut client
Syntax
hsns cut client { all | ip ip-address | mac mac-address | interface interface-type interface-number }
View
System view
Parameters
all: Forces all the current HSNS users to be offline.
ip ip-address: Forces the HSNS user with the specified IP address to be offline. Use the ip-address argument to specify a user IP address, in dotted decimal notation.
mac mac-address: Forces the HSNS user with the specified MAC address to be offline. Use the mac-address argument to specify a user MAC address, in the H-H-H format.
interface interface-type interface-number: Forces the HSNS user connected to the specified port to be offline. Use the interface-type and interface-number arguments to specify the port type and port number, respectively.
Description
Use the hsns cut client command to force a HSNS user to be offline and delete the ACL corresponding to the user.
Examples
# Force the HSNS user the IP address 10.220.1.1 to be offline.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns cut client ip 10.220.1.1
& Note:
This command will delete users from HSNS cache without affecting MAC-address table (display mac-address) stored in the switch. An explicitly link-up event (i.e. plugging the Ethernet wire) is required in order to perform a re-authentication when HSNS is working in MAC-authentication networking mode.
2.1.7 hsns enable
Syntax
hsns enable
undo hsns enable
View
System view
Parameters
None
Description
Use the hsns enable command to enable HSNS globally on the switch.
Use the undo hsns enable command to disable HSNS on the switch.
By default, HSNS is disabled on the switch.
& Note:
l Enabling or disabling HSNS takes a while. Enable or disable HSNS again only after the switch prompts that HSNS is enabled or disabled.
l Before enabling HSNS globally, verify that the connection between the switch and the ACL server is normal; otherwise, HSNS cannot be enabled.
l Configure HSNS uplink ports before enabling HSNS globally.
l You can change HSNS-related configuration only when HSNS is disabled. Enable HSNS again after the configuration is changed.
l If configured ACL servers are not reachable and server-timeout is configured large, this command may take very long time.
Examples
# Enable HSNS on the switch.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns enable
2.1.8 hsns local-address
Syntax
hsns local-address ip ip-address [ port port-number ]
undo hsns local-address
View
System view
Parameters
ip ip-address: Specifies the local interface IP address that the switch uses for communicating with the ACL server. ip-address is an IP address in dotted decimal notation.
port port-number: Specifies the UDP port that the switch uses to receive the packets from the ACL server. port-number is a port number in the range 1 to 50000.
Description
Use the hsns local-address command to specify the IP address and UDP port that the switch uses to communicate with the ACL server.
Use the undo local-address command to cancel the configuration.
By default, the switch uses the output interface address destined for the network segment of the ACL server as the local address to be used for communication with the ACL server and uses port 45899 as the UDP port.
& Note:
The local IP address that the switch uses to communicate with the ACL server must be a valid unicast address but not an all-zero address, broadcast address, multicast address, or loopback address.
Examples
# Configure the local IP address and UDP port that the switch uses for communicating with the ACL server as 192.168.0.3 and 45000, respectively.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns local-address ip 192.168.0.3 port 45000
2.1.9 hsns mode
Syntax
hsns mode { dhcp-snooping | dot1x | mac-authentication }
undo hsns mode
View
System view
Parameters
dhcp-snooping: Configures HSNS to work in the DHCP snooping mode.
dot1x: Configures HSNS to work in the 802.1x mode.
mac-authentication: Configures HSNS to work in the MAC authentication mode.
Description
Use the hsns mode command to specify the working mode of HSNS.
Use the undo hsns mode command to restore the default HSNS working mode.
By default, HSNS works in the DHCP snooping mode.
& Note:
If HSNS is configured to work in the 802.1x or MAC authentication mode, the client cannot access the network through a port whose HSNS networking mode is the Layer-3 mode.
Examples
# Configure HSNS to work in the 802.1x mode.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns mode dot1x
2.1.10 hsns retry
Syntax
hsns retry times
undo hsns retry
View
System view
Parameters
None
Description
Use the hsns retry command to specify the maximum number of packet transmission attempts from the switch to the ACL server. The specified value applies on both keepalive packets and HSNS authentication packets.
Use the undo hsns retry command to restore the default.
By default, the maximum number of packet transmission attempts from the switch to the ACL server is 3.
Examples
# Configure the maximum number of packet transmission attempts from the switch to the ACL server as 5.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns retry 5
2.1.11 hsns router-located
Syntax
hsns router-located
undo hsns router-located
View
Ethernet port view
Parameters
None
Description
Use the hsns router-located command to specify the HSNS networking mode on the port as Layer-3 mode.
Use the undo hsns router-located command to restore the default.
By default, the HSNS networking modes of all the ports of the switch are Layer-2 mode.
& Note:
l You cannot configure the HSNS networking mode of a port that is configured as a HSNS uplink port.
l If you configure a port in the Layer-3 networking mode as a HSNS uplink port, the networking mode configuration of the port will be removed.
Examples
# Configure the HSNS networking mode of GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as Layer-3 mode.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] hsns router-located
2.1.12 hsns timer check-mac-address
Syntax
hsns timer check-mac-address interval
undo hsns timer check-mac-address
View
System view
Parameters
interval: Interval at which the switch checks the user MAC address entries. It can be 0 or in the range 10 to 86400, in seconds. If interval is 0, the switch does not check the user MAC address entries.
Description
Use the hsns timer check-mac-address command to specify the interval at which the switch checks the user MAC address entries.
Use the undo hsns check-mac-address command to restore the default.
By default, the switch checks the user MAC address entries every 300 seconds.
Examples
# Configure the switch to check the user MAC address entries every 100 seconds.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns timer check-mac-address 100
2.1.13 hsns timer keep-alive
Syntax
hsns timer keep-alive interval
undo hsns timer keep-alive
View
System view
Parameters
interval: Interval at which the switch sends keepalive packets to the ACL server. It is in the range 0 to 600, in seconds.
Description
Use the hsns timer keep-alive command to specify the interval at which the switch sends keepalive packets to the ACL server.
Use the undo hsns timer keep-alive command to restore the default.
By default, the switch sends keepalive packets to the ACL server every 60 seconds.
Related commands: hsns acl-server, hsns retry.
Examples
# Configure the switch to send keepalive packets to the ACL server every 20 seconds.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns timer keep-alive 20
2.1.14 hsns timer server-timeout
Syntax
hsns timer server-timeout time
undo hsns timer server-timeout
View
System view
Parameters
time: Timeout time of ACL server packets. It is in the range 1 to 120, in seconds.
Description
Use the hsns timer server-timeout command to specify the timeout time of the ACL server packets.
Use the undo hsns timer server-timeout command to restore the default.
By default, the timeout time of ACL server packets is 10 second.
The timeout time of ACL server packets is the maximum time that the switch waits for after sending the HSNS request to the ACL server. The switch retransmits the packet if it receives no response within this timeout time. If the switch still receives no response after the maximum number of packet transmission attempts, the switch performs a primary/secondary ACL server switchover and sends the requests to the new primary server, namely, the secondary server before the switchover.
Related commands: hsns acl-server, hsns retry.
Examples
# Configure the ACL server connection timeout time as 2 seconds.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] hsns timer server-timeout 2
2.1.15 hsns uplink-port
Syntax
hsns uplink-port
undo hsns uplink-port
View
Ethernet port view
Parameters
None
Description
Use the hsns uplink-port command to specify the port as a HSNS uplink port.
Use the undo hsns uplink-port command to cancel the configuration.
By default, no Ethernet port is configured as a HSNS uplink port.
HSNS uplink ports are the switch ports connected to the DHCP server, ACL server, and other non-client devices.
& Note:
l You have to configure HSNS uplink ports before enabling HSNS globally.
l If you configure a port in the Layer-3 networking mode as a HSNS uplink port, the networking mode configuration of the port will be removed.
Examples
# Configure GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 as a HSNS uplink port.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[H3C-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] hsns uplink-port
2.1.16 soliton-dhcp-nap enable
Syntax
soliton-dhcp-nap enable
undo soliton-dhcp-nap enable
View
System view
Parameters
None
Description
Use the soliton-dhcp-nap enable command to configure fast HSNS with no ACL server.
Use the undo soliton-dhcp-nap enable command to cancel the configuration.
By default, fast HSNS with no ACL server is not enabled.
With the fast HSNS enabled with no ACL server, the switch does not obtain the ACL for the user from an ACL server. Instead, the switch determines whether the user is NAP-authenticated based on the extended options in the DHCPACK packets and applies the automatically created ACL for controlling the user access.
& Note:
l Do not enable HSNS globally before configuring fast HSNS with no ACL server.
l This configuration changes the existing HSNS configuration on the switch. It automatically enables HSNS, enables the DHCP snooping mode, deletes the existing ACL server configuration, and configures the port [Gigabit]Ethernet 1/0/1 (interface name is variant based on switch model) of the switch as a HSNS uplink port if no HSNS uplink port is configured. In addition, canceling this function does not automatically restore the configurations.
l The configuration of fast HSNS with no ACL server can be saved to a configuration file. However, the hsns enable command, instead of the soliton-dhcp-nap enable command, will be displayed in the configuration file for the configuration of fast HSNS with no ACL server.
l Fast HSNS will not automatically configure settings of DHCP snooping, local system administrators are required to configure DHCP snooping mode (i.e. dhcp-snooping trust / dhcp-snooping) before enabling fast HSNS mode.
Examples
# Enable fast HSNS with no ACL server on the switch.
<H3C> system-view
System View: return to User View with Ctrl+Z.
[H3C] soliton-dhcp-nap enable